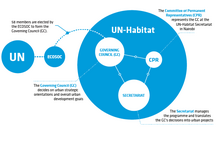
UN-Habitat is structured in three main bodies:
- the Governing Council (GC), whose role is to set the major strategic and policy directions for UN-Habitat and approve its programmes and budget,
- the UN-Habitat Secretariat – the executive body of the organization headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya – whose task is to ensure the execution of the Governing Council’s decisions and to translate them into specific strategies and programmes,
- and the Committee of Permanent Representatives (CPR), which ensures that the Governing Council’s decisions are enacted by the Secretariat within the set framework.
Governing Council (GC)
UN-Habitat's work and relationships with its partners are periodically examined in detail by the Governing Council, which is subsidiary to the UN General Assembly and serves as the intergovernmental decision-making body of UN-Habitat. It reports to the UN General Assembly through the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), and its main functions are as follows:
- Setting UN-Habitat's policies by developing and promoting policy objectives, priorities, and guidelines regarding existing and planned programmes of work in the field of human settlements;
- Overseeing working relations with partners by closely following the activities of United Nations agencies and other international organizations in the field of human settlements, and proposing ways through which the overall human settlements policy objectives within the UN system might best be achieved;
- Approving UN- Habitat's biennial work programme and budget;
The Governing Council meets every 2 years and is composed of 58 member states, which represent 5 regional groups. Member states are elected by the UN’s Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) for a period of four years.
Current member states:
- African States (16 countries): Algeria (2014), Benin (2016), Burkina Faso (2015), Central African Republic (2014), Congo (2015), Gabon (2014), Lesotho (2015), Madagascar (2016), Mali (2014), Morocco (2016), Mozambique (2014), Nigeria (2014), Somalia (2016), South Africa (2015), Uganda (2016), United Republic of Tanzania (2015)
- Western European and other States (13 countries, three vacant seats): Finland (2014), France (2016), Germany (2015), Israel (2015), Italy (2015), Norway (2016), Spain (2016), Sweden (2014), Turkey (2014), United States of America (2014)
- Latin American and Caribbean States (10 countries): Antigua and Barbuda (2016), Argentina (2014), El Salvador (2016), Brazil (2015), Chile (2014), Colombia (2016), Grenada (2014), Haiti (2015), Mexico (2015), Venezuela (2014)
- Asia-Pacific States (13 countries): Bahrain (2015), Bangladesh (2016), China (2016), India (2015), Indonesia (2014), Iran (2014), Japan (2014), Jordan (2015), Pakistan (2014), Republic of Korea (2016), Saudi Arabia (2015), Sri Lanka (2016), Thailand (2015)
- Eastern European States (6 countries, four vacant seats): Albania (2014), Russian Federation (2014)
Terms of office expire on 31 December of the years indicated (in brackets). The information above was provided by the Economic and Social Council and reflects membership status as of 26 April 2013.
The UN-Habitat Secretariat
The UN-Habitat Secretariat is the executive organ of UN-Habitat. It services the Governing Council and acts as the focal point for all human settlement matters within the United Nations system. Under the direction of the Executive Director, it is entrusted with the responsibilities set out in both Resolution 32/162 and in paragraph 228 of the Habitat Agenda.
It designs, implements, manages, and monitors UN-Habitat’s human settlements development programmes and provides the Governing Council with strategic recommendations.
It is also mandated to carry out research activities and to facilitate the exchange of information, knowledge, and best practices on urbanization questions such as global trends, effective approaches, and new technologies.
The UN-Habitat Secretariat is structured in:
- Offices that carry out management and support tasks
- Branches that handle a specific urban theme
The Committee of Permanent Representatives (CPR)
The Committee of Permanent Representatives (CPR) serves as the Governing Council's permanent inter-sessional subsidiary organ to address issues arising between the biennial Governing Council meetings. The CPR’s main functions are as follows:
- To review and monitor, within the policy and budgetary framework provided by the Governing Council, the implementation of the work programme of UN-Habitat, as well as the implementation of Governing Council decisions;
- To review the draft work programme and budget of UN-Habitat;
- To prepare draft decisions and resolutions for consideration by the Governing Council;
The Committee of Permanent Representatives has at least four regular meetings, or sessions, each year, and it is assisted by working group meetings on various topics. Its membership is open to all permanent representatives (usually ambassadors or foreign envoys) of the member states of the UN accredited to UN-Habitat.